Is it harmful when reactive oxygen species are excreted from the human body?
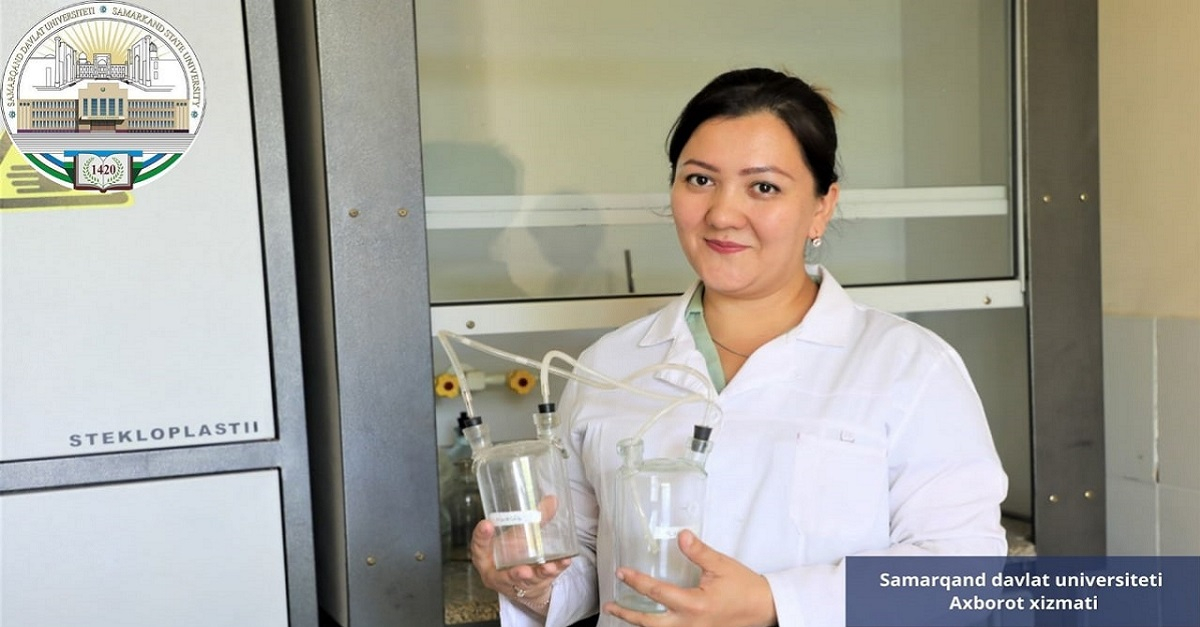

Assistant of the Department of Physical and Colloidal Chemistry of Samarkand State University Mashkhura Tagirova is engaged in scientific research on the topic “Immobilization of antioxidant enzymes in nano and microfibers”. To date, more than 20 of her articles have been published in national and international publications. 3 articles were published in journals based on Scopus and WEB of Science. Participated in international conferences in Moscow, Saratov, Novosibirsk. Studied at the graduate school of Lomonosov Moscow State University.
- It is known that many diseases can occur when the process of synthesis of reactive oxygen species in the human body is out of control, - says the famous Tagirova. - My research is designed to increase their activity and stability by immobilizing antioxidant enzymes present in living organisms.
Antioxidant enzymes are found in large quantities in plants. It is mostly in the form of protein. It is needed in industry, medicine, pharmaceuticals, manufacturing industries. Their function is to transfer oxygen in the body from an atomic form to a molecular form, in other words, turning it from a harmful species to a harmless one. The use of antioxidant enzymes is the most effective way to bind reactive oxygen species. In this regard, we pay great attention to the creation and implementation of protein-containing antioxidant systems in nano- and microfibers, which allow protecting antioxidant enzymes from inactivation. At the same time, we are studying the possibility of obtaining antioxidant enzymes with high enzymatic activity and stability in them, as well as their application in medicine and industry.
Iroda Bekmurodova
Samarkand State University
Information officer.
Photos taken by Shavkat Akramov.